RS Aggarwal Class 7 Math Thirteenth Chapter Lines and Angles Exercise 13 Solution
EXERCISE 13
(1) Find the complete of each of the following angles:
(i) 35o
Ans: let the measure of its complement be xo. Then,
x + 35 = 90
or, x = (90 – 35)
or, x = 55
(ii) 47o
Ans: let the measure of its complement be xo. Then,
x + 47 = 90
or, x = (90 – 47)
or, x = 43
(iii) 60o
Ans: let the measure of its complement be xo. Then,
x + 60 = 90
or, x = (90 – 60)
or, x = 30
(iv) 73o
Ans: let the measure of its complement be xo. Then,
x + 73 = 90
or, x = (90 – 73)
or, x = 27
(2) Find the supplement of each of the following angles:
(i) 80o
Ans: Let its supplement be xo. Then,
x + 80 = 180
or, x = (180 – 80)
or, x = 100
(ii) 54o
Ans: Let its supplement be xo. Then,
x + 54 = 180
or, x = (180 – 54)
or, x = 126
(iii) 105o
Ans: Let its supplement be xo. Then,
x + 105 = 180
or, x = (180 – 105)
or, x = 75
(iv) 123o
Ans: Let its supplement be xo. Then,
x + 123 = 180
or, x = (180 – 123)
or, x = 67
(3) Among two supplementary angles, the measure of the larger angle is 36o more than the measure of e smaller. Find their measures.
Solution: Let one angle is x and other is (x+36).
∴ x + x + 36 = 180
or, 2x = 180 – 36
or, x =
or, x = 72
Hence, required angles are 72o and (72 + 36) = 108o.
(4) Find the angle which is equal to its supplement.
Solution: Let the two angles are x and x.
2x = 180
or, x = 180/2
or, x = 90
(5) Can two angles be supplementary if both of them are:
(i) Acute = No
(ii) Obtuse = No
(iii) Right = Yes
(6) In the given figure, AOB is a straight line and the ray OC stands on it. If ∠AOC = 64o and ∠BOC = xo, find the value of x.
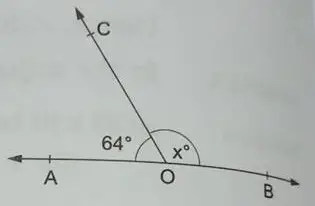
Solution: By linear property, we have:
∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180o
or, 64 + x = 180
or, x = 180 – 64
or , x = 116
Hence, ∠BOC = 116o.
(7) In the given figure, AOB is a straight line and the ray OC and OD stand on it. If ∠AOC = (2x – 10)o and ∠BOC = (3x + 20)o, find the value of x. Also, find ∠AOC and ∠BOC.
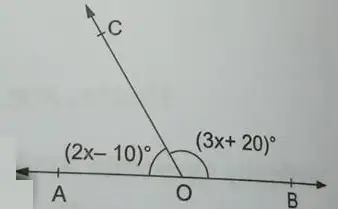
Solution: By linear property, we have,
∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180
or, (2x – 10) + (3x + 20) = 180
or, 2x – 10 + 3x + 20 = 180
or, 5x + 10 = 180
or, x = 170/5
or, x = 34
Therefore, ∠AOC = (2×34 -10) = 68 -10 = 58
∠BOC = (3×34 + 20 ) = 102 + 20 = 122.
(8) In the given figure, AOB is a straight line and the rays OC and OD stand on it. If ∠AOC = 65o, ∠BOD = 70o and ∠COD = xo, find the value of x.
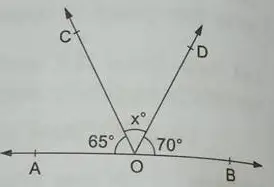
Solution: By linear property, we have,
∠AOC + ∠BOD + ∠COD = 180
or, 65 + 70 + x = 180
or, x = 180 – 135
or, x = 45
(9) In the given figure, two straight lines AB and CD intersect at a point O. If ∠AOC = 42o, find the measure of each of the angles:
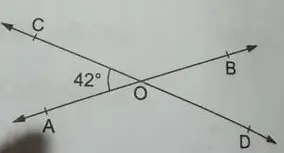
Solution: Since CD is a line and the ray OA stands on it, we have:
∠AOC + ∠AOD = 180o
or, 42o + ∠AOD = 180o
or, ∠AOD = 180o – 42o
or, ∠AOD = 138o
And ∠BOD = ∠AOC = 42o
∴ ∠COB = ∠AOD = 138o
(10) In the given figure, two straight lines PQ and RS intersect at O. If ∠POS = 114o, find the measure of each of the angles:

Solution: Since PQ is a line and the ray RS stands on it, we have:
∠POS + ∠QOS = 180o
or, 114o + ∠QOS = 180o
or, ∠QOS = 180o – 114o
or, ∠QOS = 66o
And ∠POS = ∠ROQ = 114o
∴ ∠QOS = ∠ROP = 66o
(11) In the given figure, rays OA, OB, OC and OD are such that ∠AOB = 56o, ∠BOC = 100o, ∠COD = xo and ∠DOA = 74o. Find the value of x.
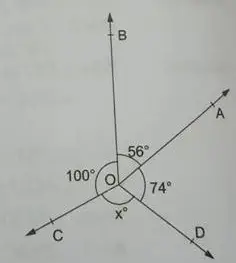
Solution: The sum of all angles around a point is 360o.
Thus, in the given figure, we have:
∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD + ∠DOA = 360o
or, 56 + 100 + x + 74 = 360
or, x + 230 = 360
or, x = 360 – 230
or, x = 130
Leave a Reply